WHAT IS A DNS (DOMAIN NAME SERVER)? Domain Name Server or we can say Domain Name System is a distributed method that helps humans to remember name of any website. Generally websites are hosted on servers using their IP Address. Humans cannot remember IP Address (numbers) all the time. That’s where DNS helps. DNS make any IP Address into normal text so anyone can remember the address of any website, according to ethical hacking professors.
Domain Name Server or we can say Domain Name System is a distributed method that helps humans to remember name of any website. Generally websites are hosted on servers using their IP Address. Humans cannot remember IP Address (numbers) all the time. That’s where DNS helps. DNS make any IP Address into normal text so anyone can remember the address of any website, according to ethical hacking professors.
Ethical hacking researcher details, on how to use nslookup for ethical hacking activities and help in finding various DNS Queries that can help us in information gathering phase of websites analyzing. DNS acts like an Address book for the internet. If you know any particular address name but don’t know their IP Address you can easily look it up in the address book. DNS works the same way.
For Instance it can be taken if user visits (webimprints.com) in a browser, computer will use DNS to receive the website IP Address which is 23.229.216.201.
DNS RECORD TYPES:-
DNS record types are generally used by DNS editor who make changes in Domain Name Server.
- A – SHOWS HOST IP ADDRESS
- MX – SHOWS TO DOMAIN MAIL SERVER
- CNAME – CANOMICAL NAME POINTS ONE OR SUB DOMAIN
- NS – SHOWS HOST NAME SERVER
- SRV – SHOWS SERVICE RECORDS
- PTR – MAPS IP ADDRESS TO HOSTNAME
- RP – RSEPONSIBLE PERSON
- HINFO – HOST INFORMATIN RECORD HOLDS
- TXT – WHERE RECORDS POINTS TO
The above mentioned DNS record types are commonly used are used to gather information about the website, mention ethical hacking consultants.
NOW THE NSLOOKUP:-
NSLOOKUP is used to figure out whether DNS record are configured properly or not.
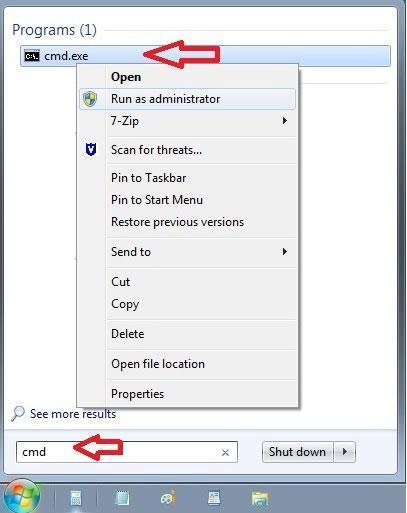
- To start using NSLOOKUP, firstly a user need to open COMMAND PROMPT.
- In Windows GO TO START MENU TYPE CMD. There you can see the COMMAND PROMPT CLICK ON CMD.EXE
- After opening CMD Type NSLOOKUP:-
- Type NSLOOKUP in the COMMAND PROMPT as shown in screenshot below:
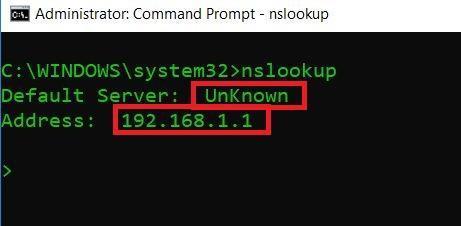
- The result will be Firstly line it will tell us the
Default Server: Unknown
And the
Address (Default Gateway).
- The Default server is Unknown because you have not set Reverse lookup zoneas, as per ethical hacking courses. Normally DNS are forward lookup queries. A reverse lookup zone is opposite to forward lookup. To enable reverse lookup you have to create PTR. To host actual domain name the PTR record maps in-addr.arpa domain name.
- The Address will be the default gateway of your ISP (INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER).
NOW YOU CAN START WITH THE DNS RECORD TYPES:
DNS RECORD TYPE = A : SHOWS THE ADDRESS RECORD
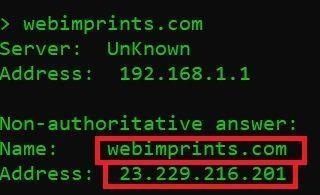
- After above command, type particular domain name
webimprints.com
As you can see in above screenshot NSLOOKUP is showing
- Name of the server – webimprints.com
- After name you can see the Address of the server which is 23.229.216.201.
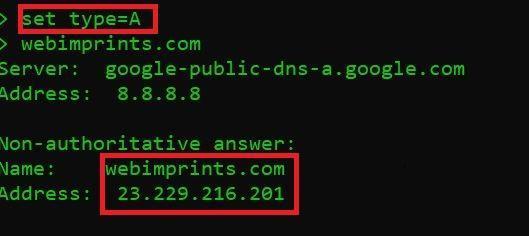
- If you type set type=A and press enter you will get the same result as shown in above image. By default NSLOOKUP command inquire the DNS server for type A records.
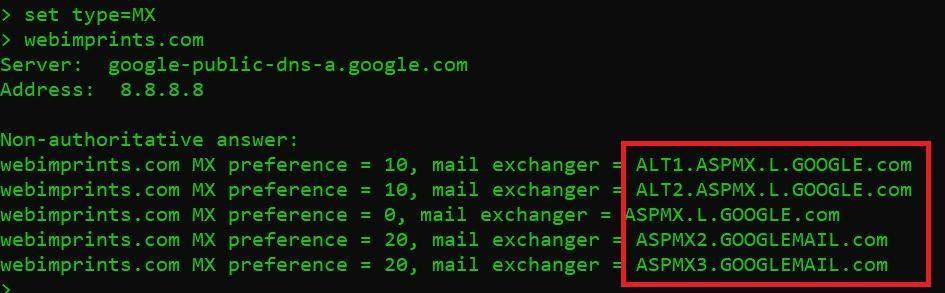
DNS RECORD TYPE = MX : SHOWS TO DOMAIN MAIL SERVER
- Type set type = MX and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
In the above screen shot you see mail server. This MX record means that website of webimprints.com is having mail exchange record. MX record or you can say it mail exchange record tells the mail delivery destination for a particular domain .i.e. webimprints.com as shown above.
- As you know that first two lines shows the rDNS (Reverse DNS) of google DNS and google DNS server IP address. Which is 8.8.8.8.
- The next 5 lines shows, 5 MX (Mail Exchange) records.
- Each MX record have its own preference and the lower numbers have a higher preference. So when mail is sent is uses MX record with the lowest preference, if lowest preference MX record is not reachable than MX record with the next high preference will be used. However if the records have same value MX preference, both MX records will be used simultaneously.
- If ALT1.ASPMX.L.GOOGL.COM is down it, will be send to ALT2.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM.
- If ALT2.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM is down it will be send to ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM and this cycle goes on until the mail send.
- Each targeted domain needs have its own A record that resolves around to your ALT1.ASPMX.L.GOOGLE.COM.
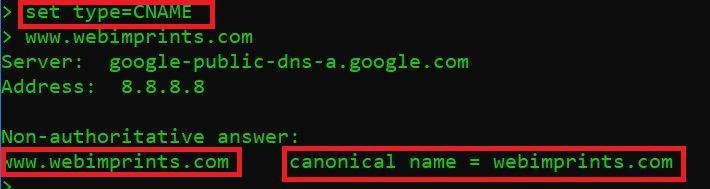
DNS RECORD TYPE = CNAME : SHOWS CANONICAL NAME
- Type set type=CNAME and press enter
- Now type https://www.webimprints.com
In the above screen shot you see a canonical name points. This CNAME record means that the website of webimprints.com is having one alias name to another.
- In CNAME canonical record matches the domain or a subdomain to different domain. Each CNAME record, DNS lookups use the target domain’s DNS resolution as to indicate a resolution.
- When a name server is requested the first DNS lookup will try to find the CNAME entry with target of name server.
- CNAME record exists so that domains can have same canonical names. You should not use a CNAME record to send/receive an email, as mail server handles the mail in abrupt manner. The targeted domain for a CNAME record should also have a normal A record.
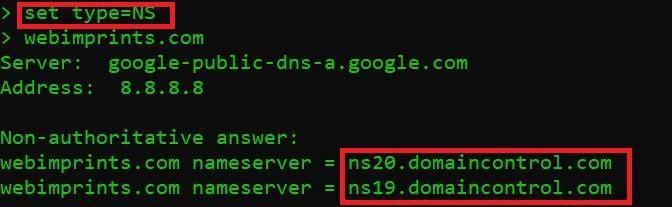
DNS RECORD TYPE = NS : SHOWS HOST NAME SERVER
- Type set type=NS and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
In the above screen shot you see a host name server. This name server is the NS record for webimprints.com domain. This NS record means that website of webimprints.com is having 2 host DNS server.
- At rooting level its get important that there should be some trustworthy name server configured to respond to queries against a domain name, explain ethical hacking specialists.
- A nameserver is a server that has DNS package installed on it. So nameserver owned by a web host that is specifically used to manage the domain names associated with their web hosting customers.
- The request to the DNS are send randomly if one host is not responding another host will be use.
DNS RECORD TYPE = SRV : INDICATE AUTHORITY FOR DOMAIN
- Type set type=SRV and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
SRV looks like:-
_service.protocol.webimprints.com SRV 10 0 5060 service.webimprint.com
_service.protocol.webimprints.com SRV 10 0 5020 service.webimprint.com
- SRV record is used to match the specific service that runs on the domain to a target domain. In some cases SRV allows direct traffic for some specific services.
- SRV normally defines name & transport protocol used in domain name.
- Priority of both records is coming out to be 10 and weight of both records is 0.
| Service | Protocol | Host | Priority | Weight | Port | Target |
| _service.protocol.webimprints.com | SRV | 10 | 0 | 5060 | service.webimprint.com | |
| _service.protocol.webimprints.com | SRV | 10 | 0 | 5020 | service.webimprint.com |
- Let us breaks the whole SRV record:-
- Service- This service element should be proceeded with an underscore (_) and followed by an (.)
- Protocol- This service element should also be proceeded with an underscore (_).
- Domain- Here name of the domain that receive original traffic.
- Priority- The number mentioned in red is used in setting up the target. You can set target according to your priority which allows to see fallback server to get the target server. Lowest numbers are always given high priority.
- Weight- If two records has same priority. Than weight will be considered as the next priority.
- Port- The services on which these ports are running TCP/UDP.
- Target- It shows the target domain and that targeted domain should have an A record to resolve an IP address.
DNS RECORD TYPE=PTR : MAP IP ADDRESS TO HOSTNAME
- Type set type=PTR and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
- PTR record allows RDNS (Reverse DNS) query, to match IP address to a domain. It works opposite to an A (Address) record. Take for example 2 hosts:
- For 172.16.0.1:
Type: PTR
Host: 1
Points to: host1.example.com
- For 172.16.0.2:
Type: PTR
Host: 2
Points to: host2.example.com
The PTR records will be shown in Control Panel like this:
| Host | Type | Point-To | TTL |
| 1.0.16.172.in-addr.arpa | PTR | host1.example.com | 1 Hour |
| 1.0.16.172.in-addr.arpa | PTR | host1.example.com | 1 Hour |
- After PTR record, always make sure that the hosts mentioned should have A records. In above example, host1.example.com should have A record pointed to 172.16.0.1 and host2.example.com with 172.16.0.2
DNS RECORD TYPE = RP : RESPONSIBLE PERSON
- Type set type=RP and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
- RP stores an email address who is holding the domain. RP is actually pointing out that the person is responsible for the host.
- The mailbox name stored with a single space between more information pointers.
- For instance: info.webimprints.com.info.people.webimprints.com to indicate info@webimprints.com.
DNS RECORD TYPE = HINFO : HOST INFORMATION HOLDS
- Type set type=HINFO and press enter
- Now type yourwebsite.com
HINFO looks like:-
Owner-name ttl class rr Hardware OS
IN HINFO PC-INTEL-700MHZ REDHAT LINUX
- HINFO records the host information in which it includes CPU type and OS.
- Such information is used in application protocols which communicates with operating system type and CPU of a computer.
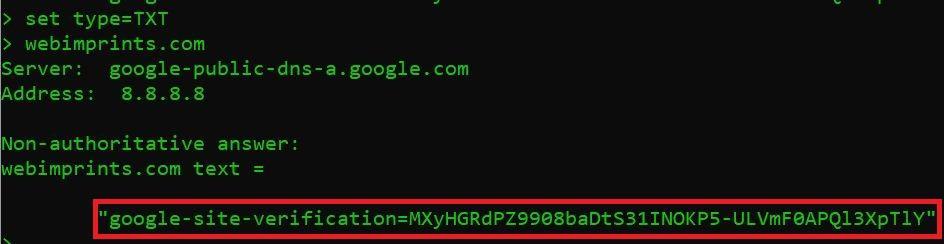
DNS RECORD TYPE = TXT
- Type set type=TXT and press enter
- Now type webimprints.com
In the above screen shot where records is pointed. These pointed record are the TXT record for webimprints.com domain.
- This TXT record means that website of webimprints.com is having records that are not used in direct traffic.
- The TXT record provides text information of some other sources on internet. This text can be human readable or machine readable.
- TXT can holds the domain name, its contact number, address.
- TXT records can have some common uses like-Domain keys (DK), Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain key identified email (DKIM).
> server 8.8.8.8 Default Server: google-public-dns-a.google.com Address: 8.8.8.8 > webimprints.com Server: google-public-dns-a.google.com Address: 8.8.8.8 Non-authoritative answer: webimprints.com text = "google-site-verification=MXyHGRdPZ908baDtS31INOP5-ULVmF0APQl3XpTlY"
- TXT records contains human readable information like:
- Name – This is the host name for your domain as marked in RED. Domain name is automatically used in your name. Your base domain will be used by default if you leave the name blank.
- Value – Now we are talking about what is marked in BLUE. If the quotes are not used in one or more strings it will be treated as separate strings.
Authoritative and Non-Authoritative DNS server
When you do nslookup for webimprints.com you get a response from one of your local DNS server configured in computer. The local DNS server configured in your computer is not the NS Server of webimprints.com. The response which we receive from the local DNS server configured on computer is shown as non-authoritative.
> server 192.168.1.1 Default Server: [192.168.1.1] Address: 192.168.1.1 > webimprints.com Server: [192.168.1.1] Address: 192.168.1.1 Non-authoritative answer: Name: webimprints.com Address: 23.229.216.201 > set type=NS > webimprints.com Server: [192.168.1.1] Address: 192.168.1.1 Non-authoritative answer: webimprints.com nameserver = ns20.domaincontrol.com webimprints.com nameserver = ns19.domaincontrol.com >
Now if we change the DNS server to one of the NS in the list and then do a nslookup against subdomain.webimprints.com, we will get an authoritative answer back, according to ethical hacking courses. This servers have authority from webimprints.com and all other nameservers are non-authoritative nameservers.

Cyber Security Researcher. Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator. He is a cyber-security researcher with over 25 years of experience. He has served with the Intelligence Agency as a Senior Intelligence Officer. He has also worked with Google and Citrix in development of cyber security solutions. He has aided the government and many federal agencies in thwarting many cyber crimes. He has been writing for us in his free time since last 5 years.