Vulnerabilities in SAP and Oracle products expose companies to crippling attacks, oil market fraud or equipment sabotage. A talk delivered at the Black Hat Europe 2015 security conference in Amsterdam shows how one simple vulnerability in an ERP suite used inside oil and gas companies can escalate to grant attackers access to the company’s entire infrastructure.
Alexander Polyakov and Mathieu Geli from ERPScan provided the presentation, which analyzed ERP systems from SAP and Oracle, advertised as complete management solutions and deployed in numerous oil and gas refineries around the globe.
The talk technically separated IT (Information Technology) from OT (Operation Technology) but also showed how intertwined the two were inside a typical oil and gas company, regardless if it implemented Oracle or SAP solutions.
The researchers are claiming that one or few vulnerabilities in the IT solutions deployed inside these companies can provide attackers with crucial access to OT infrastructure.
“For example, if you have some plant devices which collect data about oil volumes, you should somehow transfer this data to the corporate network to demonstrate it on nice dashboards managers to develop a long-term financial strategy and take decisions,” said Alexander Polyakov, ERPScan CTO.
“That’s why even if you have a firewall between IT and OT, there are some applications which are still connected, and these connections are often insecure. So, it possible to conduct such attack and jump from IT network (or even the Internet) into OT network up to SCADA systems, OPC servers, field devices, and smart meters.”
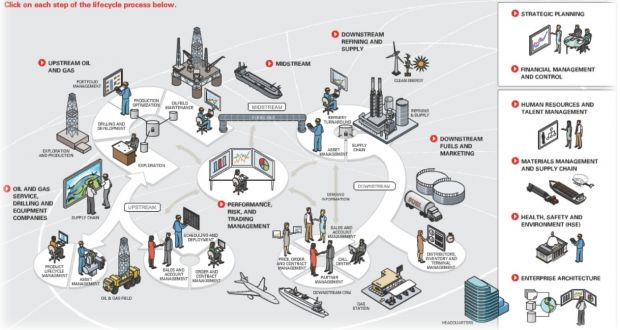
The two researchers named ERP systems, Enterprise Asset Management Systems, Manufacturing Integration Systems, Project Portfolio Planning Systems, and Laboratory Information Management Systems as the main sources of security vulnerabilities.
SAP and Oracle products put in the crosshairs
Pointing fingers, they also mention particular software solutions like SAP xMII system, SAP Plant Connect, SAP HANA, Oracle E-Business Suite platform and some widely used OPC servers such as Matricon OPC, as the main source of bugs.
But actual software vulnerabilities were not alone to blame, and the ERPScan researchers further said that misconfigurations, the presence of unnecessary privileges, and custom code added to Oracle and SAP products also provided entry or access escalation points for their theoretical attacks.
The point of the entire presentation was to show that typical air-gapped attacks are no longer needed to infiltrate and cause damage to these types of enterprises.
The days of Stuxnet are long gone, and with today’s Internet proliferation, attackers can leverage the constant online state these ERP systems sometimes need, to infiltrate IT solutions, and then slowly trickle down to OT devices and machinery to carry out devastating attacks with actual physical consequences.
The attacks can vary in results from plant destruction to equipment sabotage, and even to oil market fraud if the hackers know what they’re doing.
Making things worse is the fact that SAP systems are also deployed in around 85% of all Fortune 2000 Oil and Gas companies. With over 3,500 vulnerabilities publicly disclosed in SAP products, and other 2,500 in Oracle systems, attackers only need to craft exploit kits for these issues and find unpatched systems to attack.
Source:https://news.softpedia.com/

Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.











