A recent cybersecurity report mentions that Ryuk ransomware operators have taken a new approach to compromise the systems of their potential victims. In the most recent attacks, threat actors target hosts with remote desktop connections (RDP) exposed on the Internet, as well as using phishing emails for malware delivery.
Experts from security firm Advanced Intelligence point out that the latest Ryuk ransomware attacks compromise RDP connections to gain an initial support point on the target system with relative ease: “These attacks are based on brute force campaigns and massive password use to access vulnerable user accounts,” the experts mention.
As mentioned at the outset, threat actors also resort to phishing and the use of a campaign identified as BazaCall for malware distribution through Excel documents: “Attackers perform two-stage victim recognition, starting with defining the valuable resources of the target domain and continuing to collect information about the revenue of the compromised organization.”
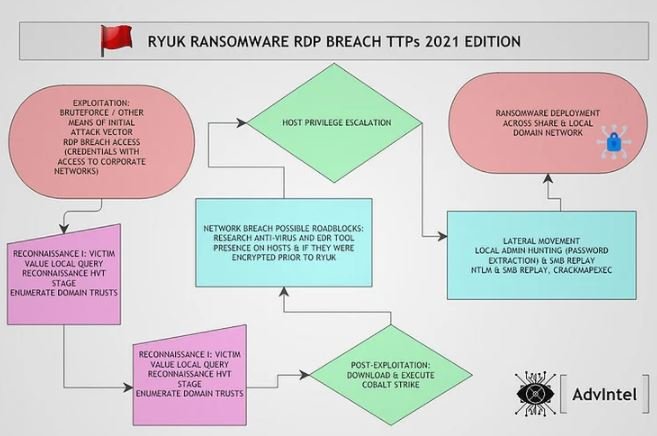
To list active directory information, threat actors use AdFind and the Bloodhound post-exploitation tool that scans relationships in an Active Directory (AD) domain to find attack paths. Hackers also employ the Cobalt Strike post-exploitation tool.
The new attack vector also involves exploiting two vulnerabilities to scale their privileges on the infected computer:
- CVE-2018-8453: Privilege escalation vulnerability on Windows 7 to 10 systems and Windows Server 2008 to 2016
- CVE-2019-1069: High-severity privilege escalation flaw in Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and 2019
It should be noted that these flaws are old and there are already the necessary patches for their correction.
Researchers also noted that attackers can use CrackMapExec, an open source tool for extracting administrator credentials: “Once hackers have compromised a local administrator account, they distribute Ryuk’s payload through Group Policy Objects, PsExec sessions from a domain controller or by using a startup item on the SYSVOL share”, experts add.
To mitigate the risk of infection, experts recommend some of the following:
- Detection of Mimikatz usage and PsExec execution on the network
- Detection of the presence of AdFind, Bloodhound and LaZagne on the network
- Confirm that operating systems and software have the latest security patches
- Implementation of multi-factor authentication mechanisms for RDP access
- Use of the principle of minimum privileges
- Install security patches against CVE-2018-8453 and CVE-2019-1069
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.

He is a well-known expert in mobile security and malware analysis. He studied Computer Science at NYU and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2003. He is actively working as an anti-malware expert. He also worked for security companies like Kaspersky Lab. His everyday job includes researching about new malware and cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in mobile security and mobile vulnerabilities.











