Redhat has just just published a risk advisory about a vulnerability in the Linux Kernel that allows for local privilege escalation. This vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2022-3910 (CVSS score: 7.4). This vulnerability is referred to be a use-after-free problem, and it can be found in io uring on the Update of Reference Count. io uring is an interface for making system calls in Linux. It made its debut for the very first time in the mainline Linux Kernel version 5.1 in the year 2019. It gives an application the ability to start system calls that may be carried out in an asynchronous manner.
CVE-2022-3910
A Use-After-Free vulnerability and a Local Privilege Escalation may be caused in the Linux kernel by incorrectly updating the reference count in the io uring function. When io msg ring is called with a fixed file, it invokes io fput file(), which incorrectly lowers its reference count. Fixed files are those that are permanently registered to the ring and must not be stored in a separate location.
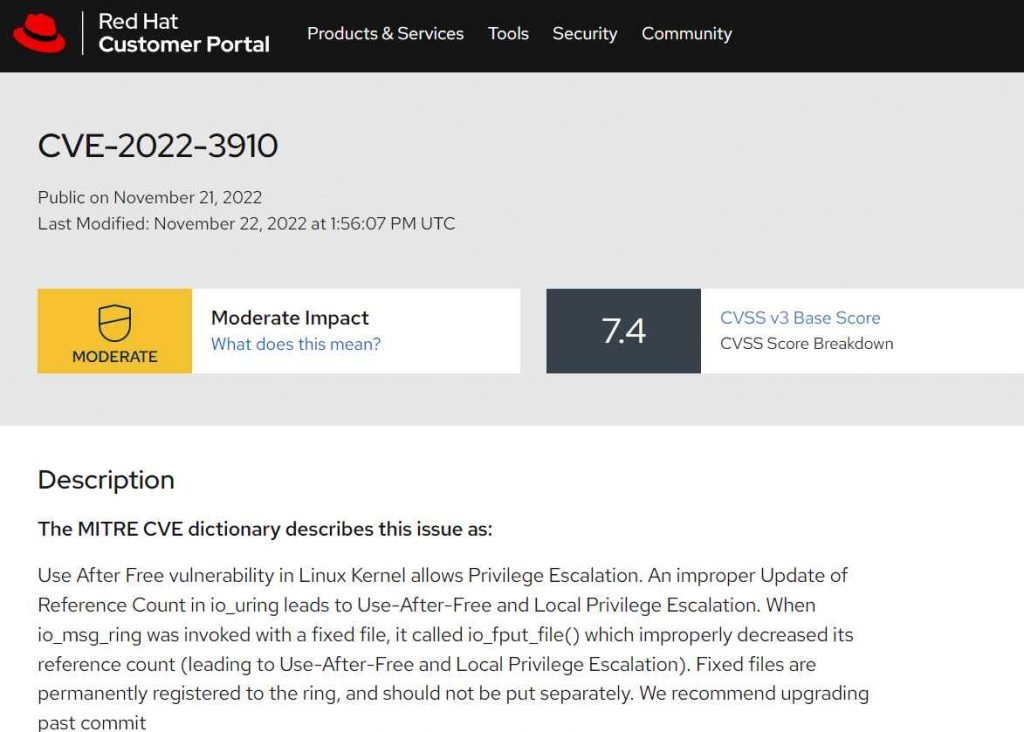
According to the official RedHat website, “When io msg ring is executed with a fixed file, it calleds io fput file(), which wrongly lowers its reference count (leading to Use-After-Free and Local Privilege Escalation).”
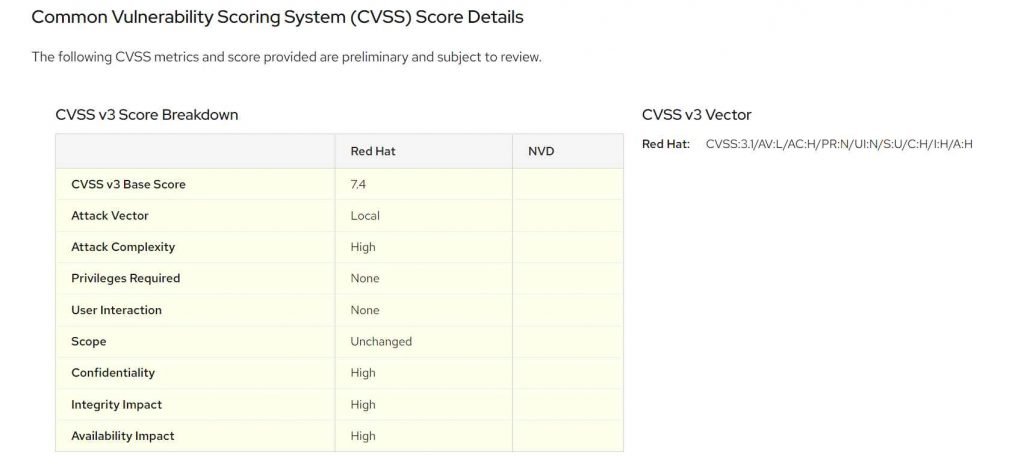
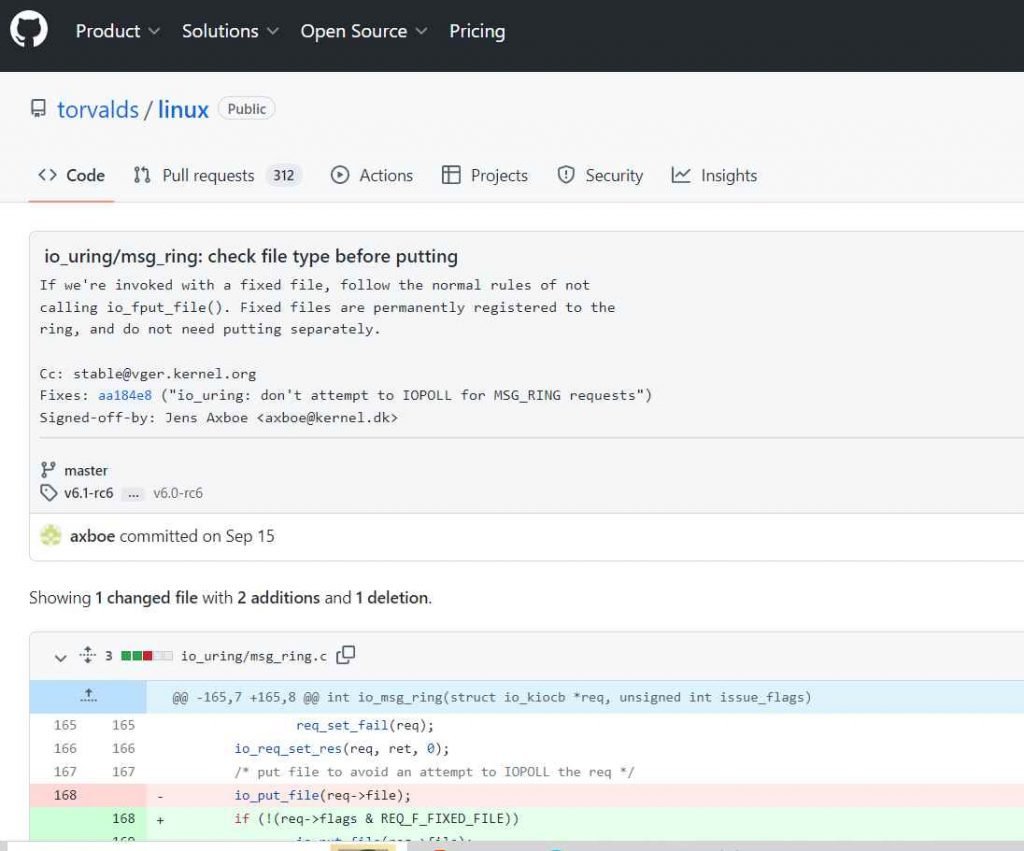
With this release, the vulnerability known as CVE-2022-3910 in the Linux kernel was patched. At the moment, the people who maintain the Linux kernel have published formal fixes to address security issues. Users are strongly encouraged to upgrade their Linux servers as soon as possible and to install patches for other distributions as soon as they become available. It is also advised that they only let trustworthy people access local systems and that they constantly check the systems that have been compromised.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











