On its March 2023 Security Patch Day, the German corporate software manufacturer SAP announced a total of 19 new security notes, five of which were designated as ‘critical’ . Security vulnerabilities in SAP products are great targets for threat actors since these products are widely utilized by huge enterprises all over the globe and may serve as entry points to incredibly valuable systems.
With a total of 425,000 clients across 180 countries, SAP is by far the most successful enterprise resource planning (ERP) software provider in the whole globe. Products such as ERP, SCM, PLM, and CRM are used by more than 90 percent of the Forbes Global 2000 companies.
To avoid data theft, ransomware attacks, and interruption of mission-critical processes and operations, the United States Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recommended administrators in February 2022 to patch a series of serious vulnerabilities affecting SAP business applications.
A memory corruption vulnerability in SAPOSCOL is one of the high-severity vulnerabilities that SAP has patched. Other high-severity vulnerabilities include a directory traversal vulnerability flaw in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform, a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) issue in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform, and an issue with SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform.
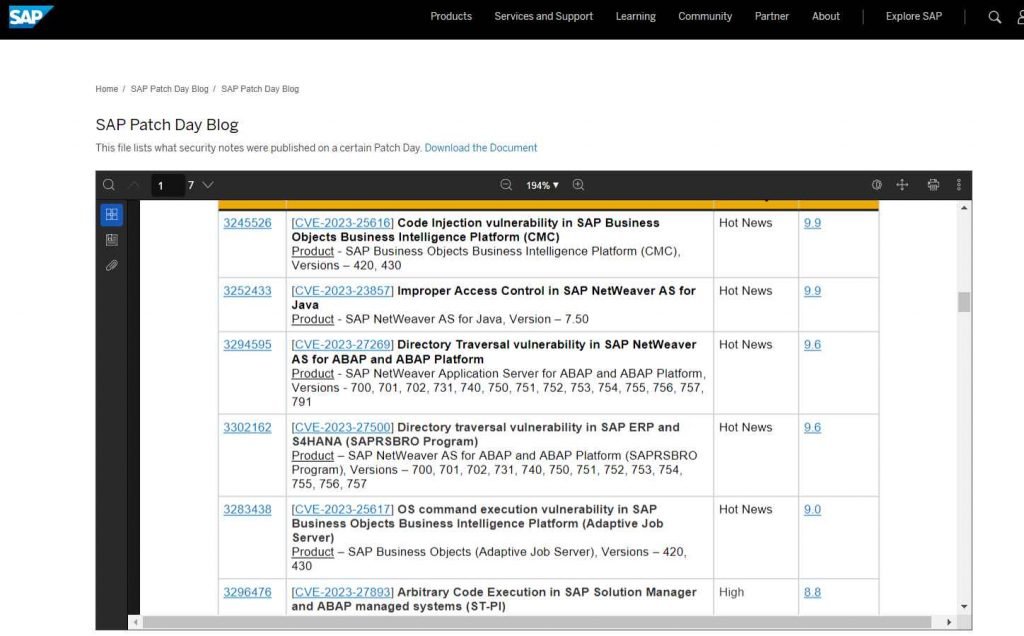
One of the major vulnerabilities is called CVE-2023-25616, and it is a code injection vulnerability in SAP Business. The CVSS score for this issue is 9.9.
Business Intelligence Platform (CMC) of Objects, impacting versions 420 and 430. Execution of a program object may lead to a vulnerability known as code injection, which gives an attacker the potential to obtain access to resources that are only accessible with additional privileges.
Incorrect access control in SAP NetWeaver AS for Java has been cited as the cause of the second serious security flaw, which has been assigned the identifier CVE-2023-23857 and received a CVSS score of 9.9. An unauthenticated attacker is able to take advantage of the vulnerability by attaching to an open interface and using an open naming and directory API to gain access to services. These services can then be used to carry out unauthorized operations that have an impact on users and services across multiple systems. In the event that the exploit is successful, the attacker has the ability to access and alter some sensitive information. But, the exploit may also be used to lock any component or operation of the system, rendering it unusable or unavailable.
The third serious vulnerability is a directory traversal issue in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform. This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.6. An adversary who does not have administrative authorizations is able to exploit the weakness by using a directory traversal flaw in a service that is exposed to them in order to rewrite the system files.
With SAP ERP and S4HANA, the directory traversal vulnerability known as CVE-2023-27500 has been rated as the fourth most severe vulnerability, with a CVSS score of 9.6. (SAPRSBRO Program).
CVE-2023-25617 is an OS command execution vulnerability that exists in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform. It has a CVSS score of 9.0 and is ranked as the fifth most significant vulnerability (Adaptive Job Server). When program objects execution is enabled, the bug enables the remote execution of arbitrary commands on Unix. Authenticated users with scheduling rights can take advantage of this vulnerability by using the Business Intelligence Launchpad, the Central Management Console, or a custom application based on the public Java SDK.

Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.











